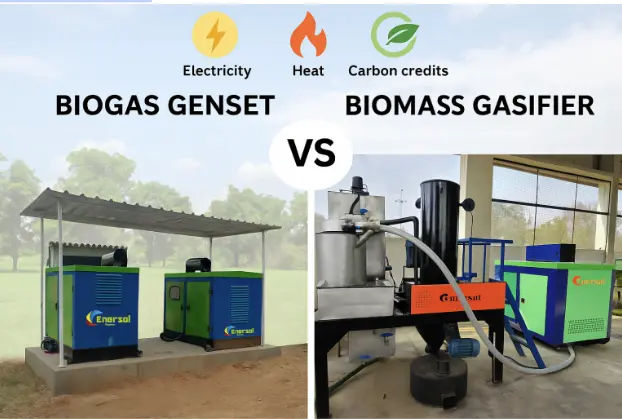
The Energy Challenge & the Untapped Opportunity
India generates over 500 million tonnes of agricultural residue every year—much of which is either burned in the open or left to decay, releasing CO₂, methane, and harmful particulates. Meanwhile, rural and industrial users still rely heavily on expensive fossil fuels and unreliable grid power. Converting crop residue into clean, affordable energy through biomass gasification turns an environmental liability into a valuable, low-carbon resource.
What is a Biomass Gasifier?
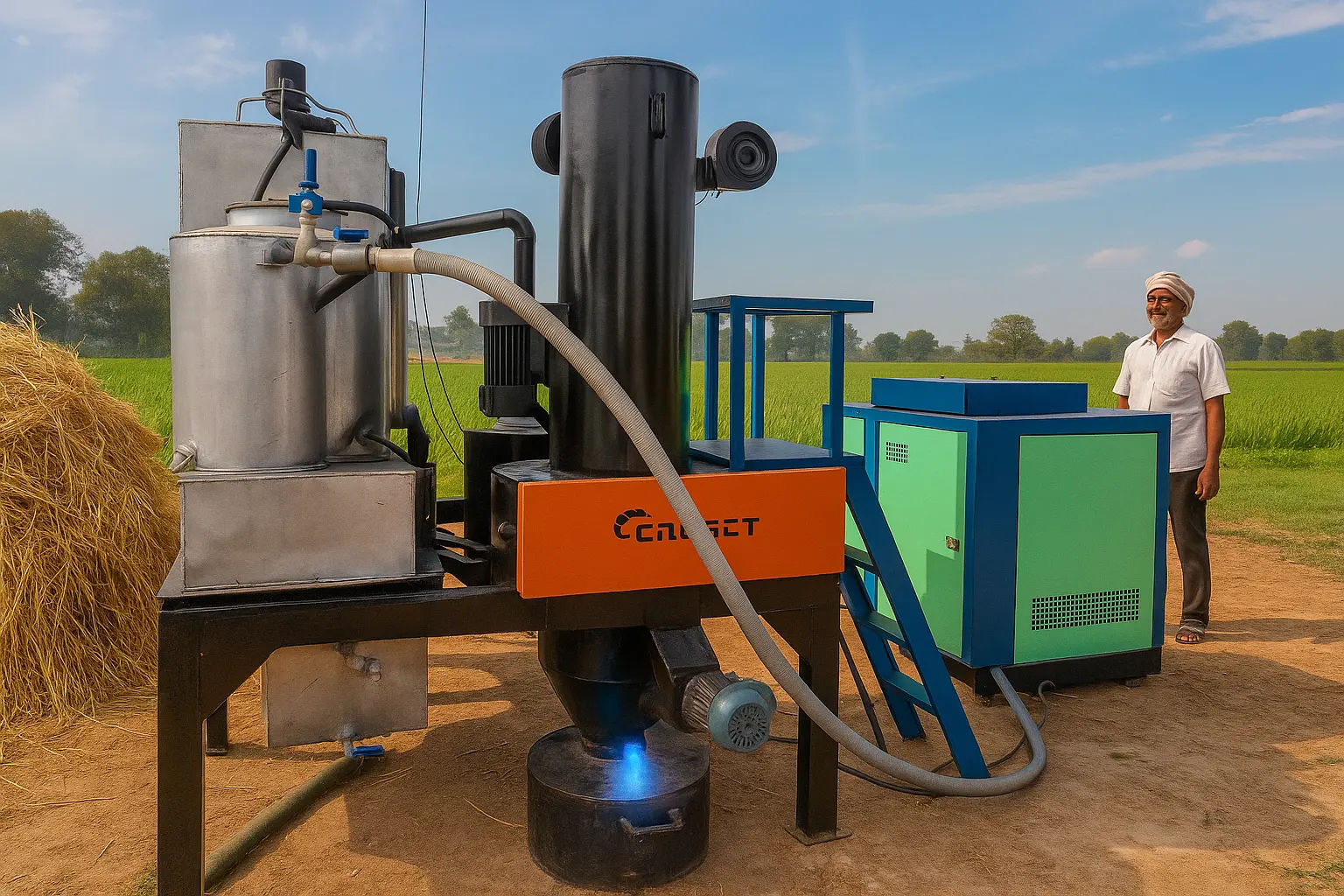
A biomass gasifier is an engineered reactor that converts solid organic matter—such as paddy straw, wheat stubble, cotton stalk, coconut shells, or sawdust—into a combustible gas called producer gas (a mix of CO, H₂, CH₄, and N₂). Think of it as a high-efficiency, controlled bonfire inside a sealed chamber: instead of smoke and ash, you get a versatile gaseous fuel.
This green technology offers a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative to traditional fuels like LPG and diesel, especially in remote or off-grid locations.
ESB-R10 Biomass Gasifier
How Does It Work?
Crop residue is fed into the gasifier
Heated at high temperatures in low oxygen
Produces clean-burning producer gas
Generates electricity or heat
No LPG, No Diesel – just pure Power from Agricultural Waste!
Why Crop Residue?
Abundant & Affordable
India generates millions of tons of crop residue each year, much of which is left unused or mismanaged—often contributing to air pollution and public health issues. This agricultural waste is readily available after every harvest and comes at minimal or no cost, making it an ideal fuel source without requiring dedicated energy crops.
Reduces Open-Field Burning
Using crop residue in biomass gasifiers helps eliminate the need for stubble burning, drastically reducing pollutants like PM₂.₅ and NOₓ—leading to cleaner air and healthier living conditions.
Creates Income for Farmers
Instead of going to waste, agricultural residue becomes a valuable, sellable resource—offering an additional income stream for farmers and encouraging sustainable practices.
Promotes Circular Economy
The by-product, biochar, is rich in carbon and nutrients. When returned to the soil, it improves fertility, enhances moisture retention, and locks carbon into the ground—closing the loop between energy and agriculture.
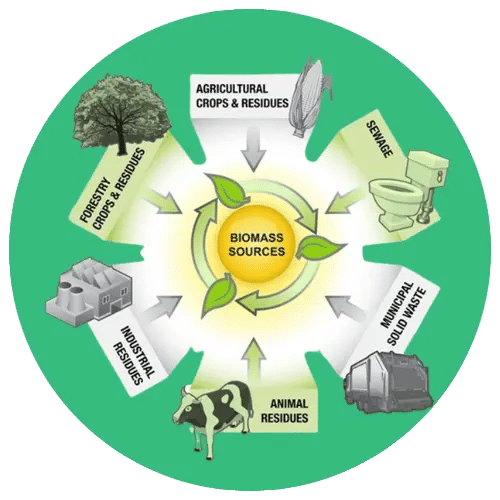
Common Types of Crop Residue Used as Fuel
Biomass gasifiers are highly versatile and can run on a wide variety of locally available agricultural residues, such as:
These fuels are low-cost, non-toxic, and widely available across India.
Environmental & Economic Benefits
Environmental Impact
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions and black carbon
- Helps meet carbon credit and sustainability targets
- Replaces fossil fuels with renewable alternatives
- Minimizes deforestation for firewood
Economic Impact
- Saves up to 60–70% on LPG, diesel, or furnace oil costs
- Lowers cooking and process heat expenses
- Empowers local job creation
- Creates additional revenue streams for farmers
Applications in India
-
Commercial Kitchens
Dhaba, canteen, langar, hostels, food stalls
-
Rural Microgrids
Biomass gasifiers power decentralized electricity
-
Agro-Processing Units
Tea dryers, spice mills, and rice mills
-
Industrial Heat
Ceramic kilns, foundries, small manufacturing
-
Carbon Farming
Biochar application in sustainable agriculture
-
Village Power
Irrigation during day, home lighting at night
Why Choose ESB-R Biomass Gasifier?
At Enersol Biopower, our ESB-R Biomass Gasifier range is trusted across India for its efficiency, durability, and carbon-saving performance. Here's what sets us apart:
Whether it’s for a small tea stall or a 1 MW rural power plant, the ESB-R Gasifier is built to perform and built to last.
Powering the Future with Crop Waste
A Biomass Gasifier is not just a machine — it’s a smart, green solution to two of India’s biggest challenges: crop residue disposal and energy access.
Contact Us to Learn More